The blast freezer is a type of freezer storage which rapidly brings down the temperature of usually cooked or fresh produce, freezing it very quickly to lock in the taste and nutrition of the food for optimum quality for consumers.
- Home
- About
- Projects


Work Package 4
Development of a sustainable and inclusive value-chain for smallholder dairy farmers in the Republic of Mauritius
Learn More >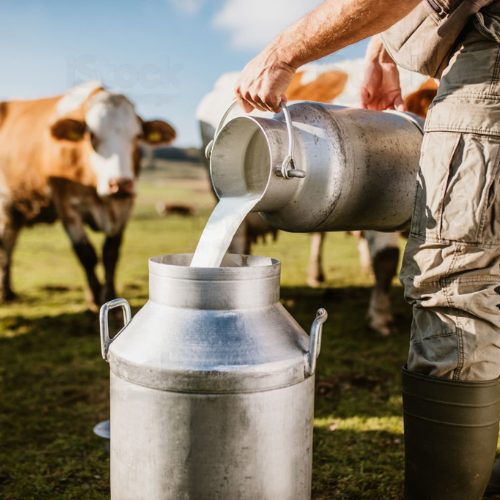
Work Package 5
Curriculum development and implementation of a Top-up programme in Agricultural Science and Technology for Rodrigues
Learn More >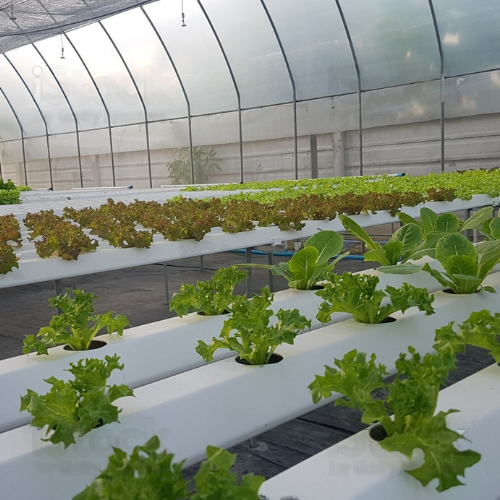
- Contact Us
- Home
- About
- Projects


Work Package 4
Development of a sustainable and inclusive value-chain for smallholder dairy farmers in the Republic of Mauritius
Learn More >
Work Package 5
Curriculum development and implementation of a Top-up programme in Agricultural Science and Technology for Rodrigues
Learn More >
- Contact Us

















